
How to Change Your Car Battery: Expert Tips & Steps
A dead or dying car battery is one of the most common automotive problems you’ll encounter, and fortunately, it’s also one of the easiest to fix yourself. Whether your battery won’t hold a charge or your car won’t start on a cold morning, learning how to change a car battery can save you hundreds of dollars in mechanic fees and get you back on the road quickly. Most car owners can complete this task in 15 to 30 minutes with just a few basic tools and safety precautions.
Replacing your car battery isn’t just about saving money—it’s about understanding your vehicle better and gaining confidence in basic automotive maintenance. This guide walks you through everything you need to know, from identifying battery problems to safely removing the old battery and installing a new one. We’ll cover the tools you’ll need, step-by-step instructions, and expert tips to ensure the job is done correctly.

Signs Your Car Battery Needs Replacement
Before you start the replacement process, it’s important to confirm that your battery is actually the problem. A weak or dead battery will exhibit several telltale signs that alert you to potential issues. The most obvious indicator is when your car won’t start at all, or it struggles to turn over with a slow cranking sound. You might also notice that your dashboard lights are dimmer than usual, or they flicker when you turn on the headlights.
Other warning signs include a clicking sound when you turn the key, a swollen or bloated battery case, or a rotten egg smell coming from under the hood—this sulfurous odor indicates battery acid leakage. If your car has been sitting unused for an extended period, or if you’ve noticed that electrical accessories like power windows or the stereo are operating sluggishly, your battery may be losing its charge capacity. Most car batteries last between three to five years, so if yours is approaching that age range, it’s wise to have it tested at an auto parts store, which typically offers free testing services.
Tools and Materials You’ll Need
Gathering the right tools before you begin ensures a smooth, safe replacement process. You won’t need an extensive collection of specialized equipment—most of these items are common household tools or inexpensive automotive supplies. Here’s what you should have on hand:
- Socket wrench set (typically 8mm, 10mm, or 13mm depending on your vehicle)
- Adjustable wrench as a backup option
- Battery terminal cleaner or a wire brush for corrosion removal
- Safety glasses or goggles to protect your eyes from acid splashes
- Heavy-duty gloves (nitrile or leather) to protect your hands
- New replacement battery (matching your vehicle’s specifications)
- Battery terminal protector spray or petroleum jelly
- Baking soda and water for cleaning corrosion
- Small container or drain pan to catch any battery acid
- Battery charger (optional, but helpful for maintenance)
Before purchasing a new battery, check your vehicle’s owner manual or visit an auto parts retailer to confirm the correct battery size, type, and cold cranking amps (CCA) rating for your specific make and model. Installing an incorrect battery can affect your vehicle’s performance and may not provide adequate starting power.
Safety Precautions Before Starting
Car batteries contain sulfuric acid and can deliver a significant electrical charge, so safety is paramount when handling them. Always wear safety glasses and gloves to protect yourself from acid splashes and sharp battery terminals. Remove any metal jewelry, watches, or rings that could create an electrical short if they contact both terminals simultaneously.
Turn off your engine completely and ensure it has cooled for several minutes before beginning work. Disconnect any auxiliary devices like phone chargers or GPS units from your vehicle’s power outlet. If your car has an alarm system, be aware that disconnecting the battery may trigger it temporarily. Work in a well-ventilated area, preferably outdoors or in a garage with the door open, as batteries can emit potentially harmful fumes.
Never smoke or create sparks near a car battery, as hydrogen gas released during charging or discharging is highly flammable. If you accidentally spill battery acid on your skin, rinse immediately with large amounts of water and seek medical attention. For more detailed safety information and building code compliance, consult This Old House’s home improvement guides.
Step-by-Step Battery Replacement Process
Now that you’re prepared with tools and safety knowledge, let’s walk through the actual replacement procedure. This process applies to most vehicles, though specific details may vary slightly depending on your car’s make and model. Always consult your owner’s manual for any vehicle-specific instructions or warnings.
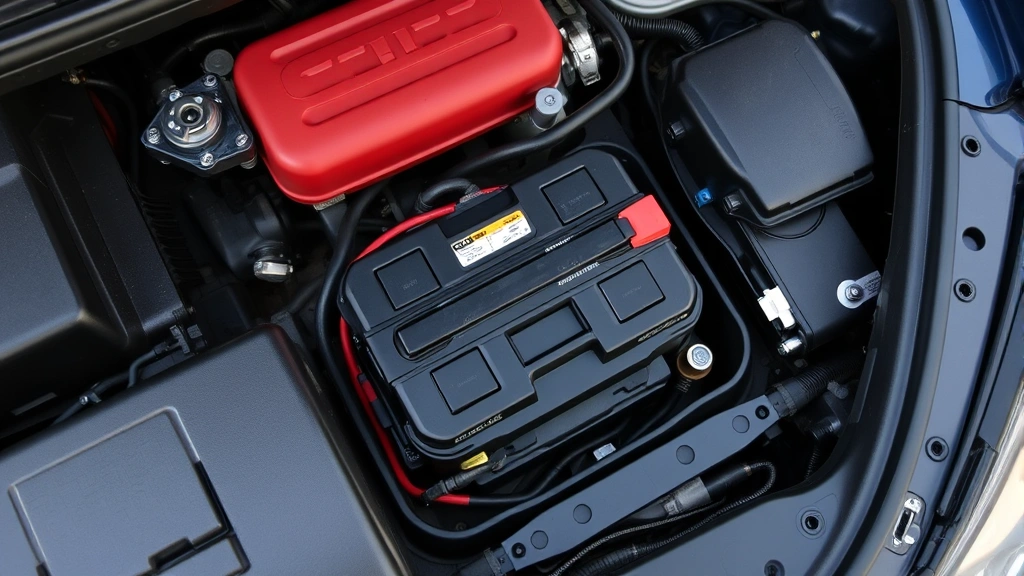
The first step is to locate your battery, which is typically under the hood on the driver’s or passenger’s side. Open your hood and visually inspect the battery to identify the positive terminal (marked with a red cover or + symbol) and the negative terminal (marked with a black cover or − symbol). Take a moment to examine how the battery is secured—most batteries are held in place by a metal bracket or clamp that you’ll need to remove.
Disconnecting the Old Battery
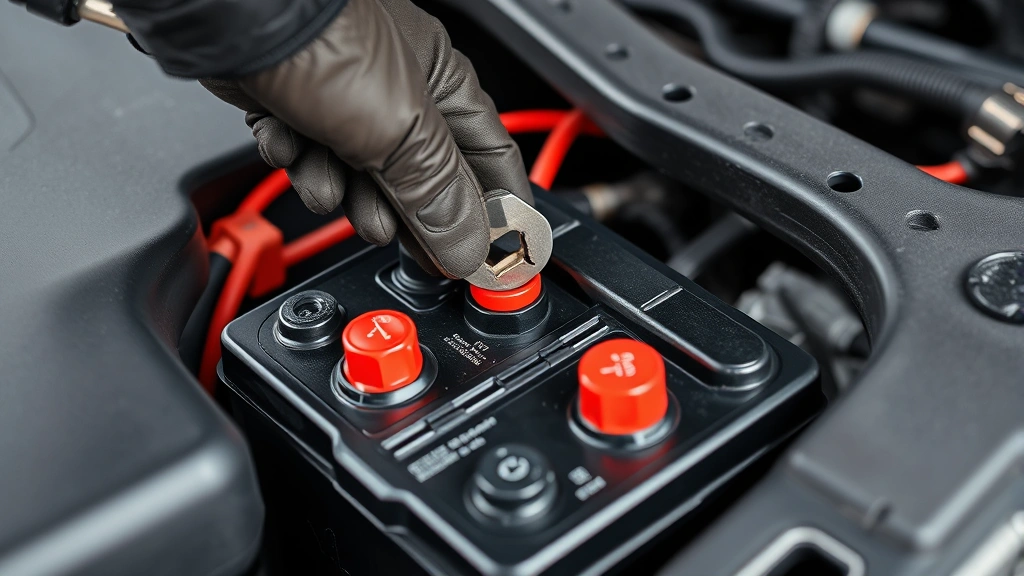
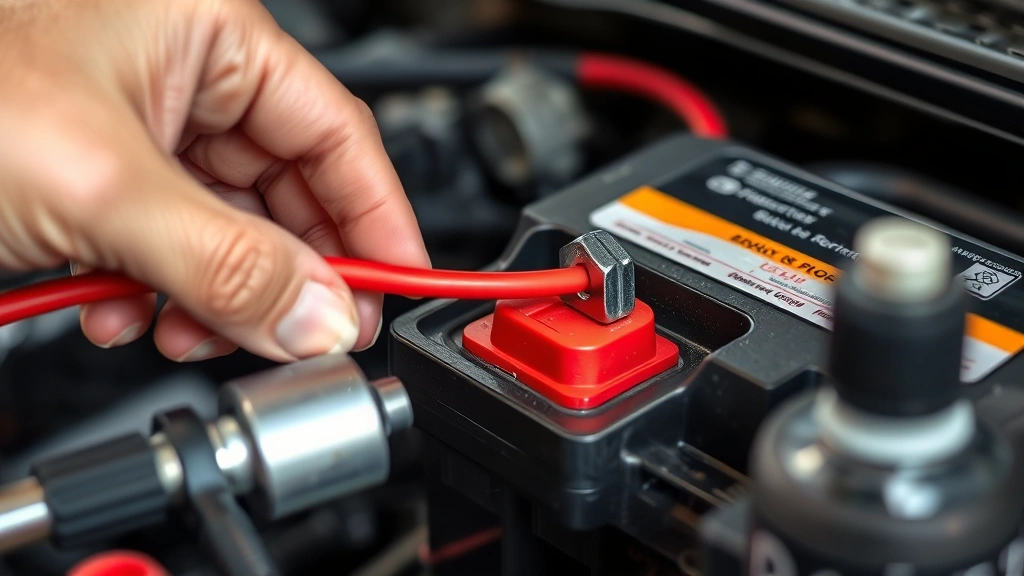
This is the most critical step in the process, and it must be done in the correct order to prevent electrical damage or shock. Always disconnect the negative terminal first. Using your socket wrench, loosen the nut on the negative (black) terminal and carefully wiggle the cable away from the post. Move the negative cable to the side where it cannot accidentally make contact with the battery terminal.
Next, disconnect the positive (red) terminal using the same process. This two-step disconnection order is crucial because it prevents electrical arcing or short circuits. Once both cables are disconnected, remove any brackets or straps holding the battery in place. These are typically held with one or two bolts that can be removed with your socket wrench.
Carefully lift the old battery straight up and out of its compartment. Car batteries are heavy—typically weighing 30 to 50 pounds—so use proper lifting technique and consider asking someone to help you. Place the old battery in a safe location away from children and pets. Many auto parts stores will accept old batteries for recycling when you purchase a new one, so ask about their take-back program.
Before installing the new battery, clean the battery tray and terminal posts using a wire brush and baking soda solution if corrosion is present. This ensures good electrical contact and extends your new battery’s lifespan. If you’re interested in learning about other electrical maintenance tasks like wiring an outlet, similar attention to detail and safety precautions apply.
Installing Your New Battery
Carefully position your new battery into the battery compartment, ensuring it sits flat and secure. The battery should be oriented the same way as the old one, with terminals facing the same direction. Once positioned correctly, install any brackets or clamps that hold the battery in place, tightening them securely but not excessively.
Now comes the reconnection process—and remember, this order is opposite to disconnection. Always connect the positive terminal first. Place the positive (red) cable onto the positive terminal post and tighten the nut securely with your socket wrench. The connection should be snug enough that the cable doesn’t wiggle, but don’t over-tighten as this can damage the terminal.
Next, connect the negative (black) cable to the negative terminal and tighten it securely. After both cables are connected, apply a thin layer of battery terminal protector spray or petroleum jelly to the connections. This coating helps prevent corrosion and extends the life of your terminals. Close your hood and start your engine to verify that everything is working correctly.
Post-Installation Tips and Maintenance
After successfully installing your new battery, take a few moments to verify that all electrical systems are functioning properly. Check that your dashboard lights, headlights, interior lights, and windshield wipers all operate as expected. If your vehicle has an infotainment system, you may need to re-enter your preferred settings or re-pair your Bluetooth devices, as these are often reset when power is disconnected.
Your new battery may take a few charging cycles to reach peak performance, so don’t be alarmed if it seems slightly less powerful during the first week of use. Normal driving will charge the battery fully. To maximize your battery’s lifespan, keep your vehicle’s charging system in good working order, avoid leaving electrical accessories running when the engine is off, and have your battery tested annually, especially as it approaches the three-year mark.
For comprehensive guidance on automotive maintenance, visit Family Handyman’s car battery replacement article. Additionally, if you’re interested in maintaining other aspects of your home and vehicle, our guide on home maintenance basics at FixWise Hub Blog covers various DIY projects you can tackle yourself.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If your car still won’t start after battery replacement, several factors could be responsible. First, verify that both battery cables are connected tightly and securely. A loose connection can prevent the battery from delivering power to the starter motor. If connections are secure, check that you used the correct battery type and size for your vehicle—an incompatible battery may not provide sufficient power.
If you see corrosion on the battery terminals that resembles white, blue, or green crusty buildup, clean it away with a wire brush and baking soda solution before troubleshooting further. Corroded terminals prevent proper electrical contact and can cause starting problems even with a new battery. If your vehicle’s dashboard lights are on but the engine won’t turn over, you may have an alternator problem rather than a battery issue—the alternator is responsible for charging the battery while your engine runs.
Some vehicles with advanced electrical systems may require battery registration or coding after replacement. Consult your owner’s manual or visit a dealership if your car displays warning messages on the dashboard after battery installation. For automotive electrical questions and professional advice, check resources like AutoZone’s battery selection guide.
If you notice that your new battery is draining quickly even when the car is off, you may have a parasitic drain—an electrical component drawing power when it shouldn’t. This requires more advanced electrical diagnostics, so consider having a professional mechanic investigate the issue.
FAQ
How long does it take to change a car battery?
Most people can complete a car battery replacement in 15 to 30 minutes, depending on their experience level and the specific vehicle design. Some cars have batteries in less accessible locations that may take longer to reach and remove.
Can I change my car battery in the rain?
While it’s not ideal, you can change your battery in light rain if necessary. However, avoid working during heavy downpours or thunderstorms, as wet conditions increase the risk of electrical hazards. Always ensure you’re wearing protective gloves and glasses for safety.
What should I do with my old car battery?
Most auto parts retailers, including those at major retailers like Lowe’s automotive section, accept old batteries for recycling when you purchase a replacement. Some stores offer core charges or discounts for turning in your old battery. Never dispose of a car battery in regular trash, as they contain hazardous materials.
How do I know what battery size my car needs?
Check your vehicle’s owner manual for the correct battery specifications, or visit an auto parts store where staff can identify the right battery based on your vehicle’s make, model, and year. The battery group size, voltage, and cold cranking amps (CCA) rating are critical specifications.
Will changing my battery erase my car’s computer settings?
Disconnecting the battery may reset some settings like clock time, radio presets, and seat position memory, but it won’t erase your vehicle’s engine computer data or service records. Modern vehicles typically retain this critical information in permanent memory.
How often should I replace my car battery?
Most car batteries last three to five years, depending on climate conditions, driving habits, and how well you maintain your vehicle’s electrical system. Extreme heat or cold climates may shorten battery lifespan significantly.
